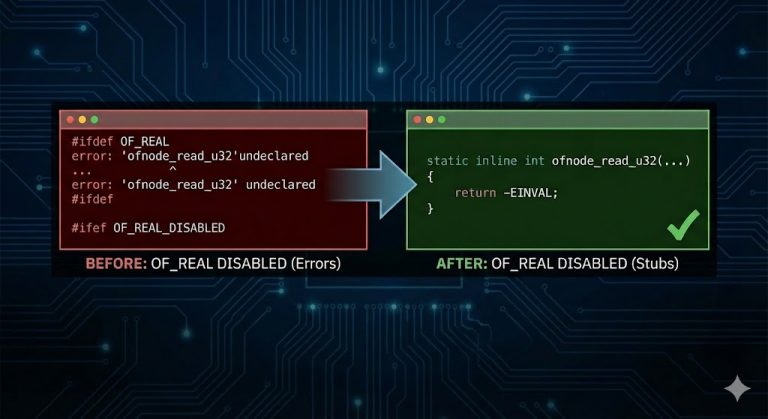
Cleaning Up ext4l: Organizing the Compatibility Layer
We’ve been working to improve the structure of the ext4l filesystem implementation in U-Boot, specifically targeting the large compatibility layer that allows us to reuse Linux kernel code. We’ve just posted a new 33-patch series that reorganises the compatibility stubs, moving them out of the monolithic ext4_uboot.h and into their proper locations within include/linux/. The…